We are now receiving orders for ECO,Paper vol.2
Bagasse
What is bagasse?
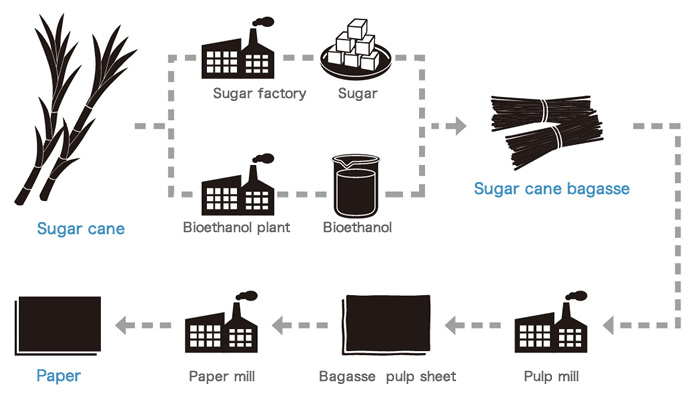
After extracting sugar juice or biomass ethanol from sugar canes, a huge amount of residual wastes consisting of stalks and leaves are generated. This residue is called “bagasse,” and approximately 1 billion ton (dry weight equivalent) of bagasse is generated for every 1.2 billion tons of sugar cane produced every year. While part of it is burned in boiler and is used as the power source for producing sugar, the rest is discarded. Because this surplus bagasse is basically plant fiber, it can be turned into pulp that can be used as the raw material for manufacturing paper along with wood.
From sugar cane to bagasse pulp
Environmental benefits of using bagasse
- Utilization of unused resources and recycling of waste -
Bagasse is a by-product of sugar production, and its excess is treated as waste.
- An alternative of wood pulp = Protection of forest resources -
You can reduce the amount of wood used by utilizing bagasse as the raw material for paper.
- No emission of organic chlorine compounds -
We do not use chlorine in bleaching bagasse.
(= ECF:Elemental Chlorine Free: Chlorine-free bleaching)
- Reduction of CO2, and energy conservation -
At our manufacturing factory of bagasse pulp, less energy is required for harvesting, gathering, pick-up, and transportation compared with factories that use wood or non-wood as raw materials because the raw material, bagasse, is transported from the neighboring sugar factory by a conveyor belt. It has been estimated that CO2 emission can be reduced by approximately 179kg for every ton of pulp produced this way.



